In 2025, glp 1 medications have emerged as the most significant breakthrough in weight loss treatment, offering hope to millions struggling with obesity and weight-related health conditions. These powerful medications, originally developed for diabetes management, have transformed the landscape of weight management with their remarkable ability to help patients lose significant amounts of weight.
Important Disclosure About Compounded GLP-1 Medications: This comprehensive guide covers both FDA-approved brand name GLP-1 medications and compounded GLP-1 medications available through services like AlynMD. It’s crucial to understand that compounded GLP-1 medications are not FDA-approved and are prepared by licensed compounding pharmacies when commercially manufactured versions are unavailable or medically inappropriate for individual patients. While compounded medications contain the same active ingredients as their brand-name counterparts, they are accessed through different regulatory pathways and may have variability in potency, sterility, and safety compared to FDA-approved versions. Compounded GLP-1s should only be used under proper medical supervision and when commercial alternatives are not suitable or accessible. Patients considering any GLP-1 treatment should discuss both FDA-approved and compounded options with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate and safe treatment approach.
This guide will equip you with essential knowledge about how these medications work, their effectiveness, potential side effects, and practical considerations for 2025. Whether you’re exploring treatment options or currently using GLP-1 therapy, you’ll find evidence-based information to make informed decisions about your weight management journey.
Table of Contents
- What Are GLP-1 Medications?
- How GLP-1 Medications Work for Weight Loss
- Available GLP-1 Medications in 2025
- Side Effects and Safety Profile
- Dosing and Administration
- Clinical Evidence and Research Updates
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Choosing Between Brand and Compounded Options
- When to Consult Your Healthcare Provider
What Are GLP-1 Medications?
Glucagon like peptide 1 receptor agonists are a class of medications that mimic the action of a natural hormone called GLP-1, which plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar and appetite. The journey of these medications began in 2005 when the FDA first approved exenatide (Byetta) for diabetes treatment, marking the beginning of a revolution in metabolic medicine.
GLP-1 is naturally produced by specialized cells in your intestine called enteroendocrine L-cells. When you eat, these cells release GLP-1 to help control blood sugar levels and signal satiety to your brain. However, natural GLP-1 has an extremely short half-life of approximately 2 minutes, being rapidly broken down by enzymes like dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4).
The evolution from diabetes treatment to weight loss breakthrough represents one of medicine’s most remarkable developments. Researchers discovered that patients taking GLP-1 medications for diabetes consistently experienced significant weight loss as a “side effect.” This observation led to dedicated weight loss trials and eventually FDA approvals for obesity treatment.
Synthetic GLP-1 medications are engineered to resist the enzymes that quickly break down natural GLP-1, allowing them to remain active in your body for much longer periods. This extended action makes them practical as therapeutic agents, typically requiring only weekly injections for most formulations.
How GLP-1 Medications Work for Weight Loss
GLP-1 medications achieve weight loss through four primary mechanisms that work synergistically to reduce food intake and improve metabolic function.
Glucose-Dependent Insulin Secretion: When blood sugar levels rise after eating food, GLP-1 medications stimulate pancreatic beta cells to release insulin. This mechanism is glucose-dependent, meaning it only occurs when blood sugar is elevated, significantly reducing the risk of low blood sugar episodes.
Glucagon Suppression: These medications inhibit the release of glucagon, a hormone that typically raises blood sugar by triggering glucose release from the liver. By suppressing glucagon when blood sugar is high, GLP-1 medications help maintain better blood sugar control.
Delayed Gastric Emptying: Perhaps the most noticeable effect for weight loss, GLP-1 medications slow the rate at which food moves from your stomach into your small intestine. This creates a prolonged feeling of fullness after eating and helps control portion sizes naturally.
Central Appetite Suppression: GLP-1 receptors in the brain, particularly in areas that control hunger and satiety, receive signals that reduce appetite and food cravings. Many patients report a dramatic decrease in food thoughts and the ability to feel satisfied with smaller portions.
The timeline of effects varies among individuals, but most patients notice appetite changes within the first week of treatment. The full weight loss effects typically develop over several months as the body adjusts to the medication and patients naturally reduce their food intake.
Weight loss dosing differs significantly from diabetes dosing, with obesity treatment typically requiring higher doses to achieve optimal appetite suppression and gastric emptying effects.
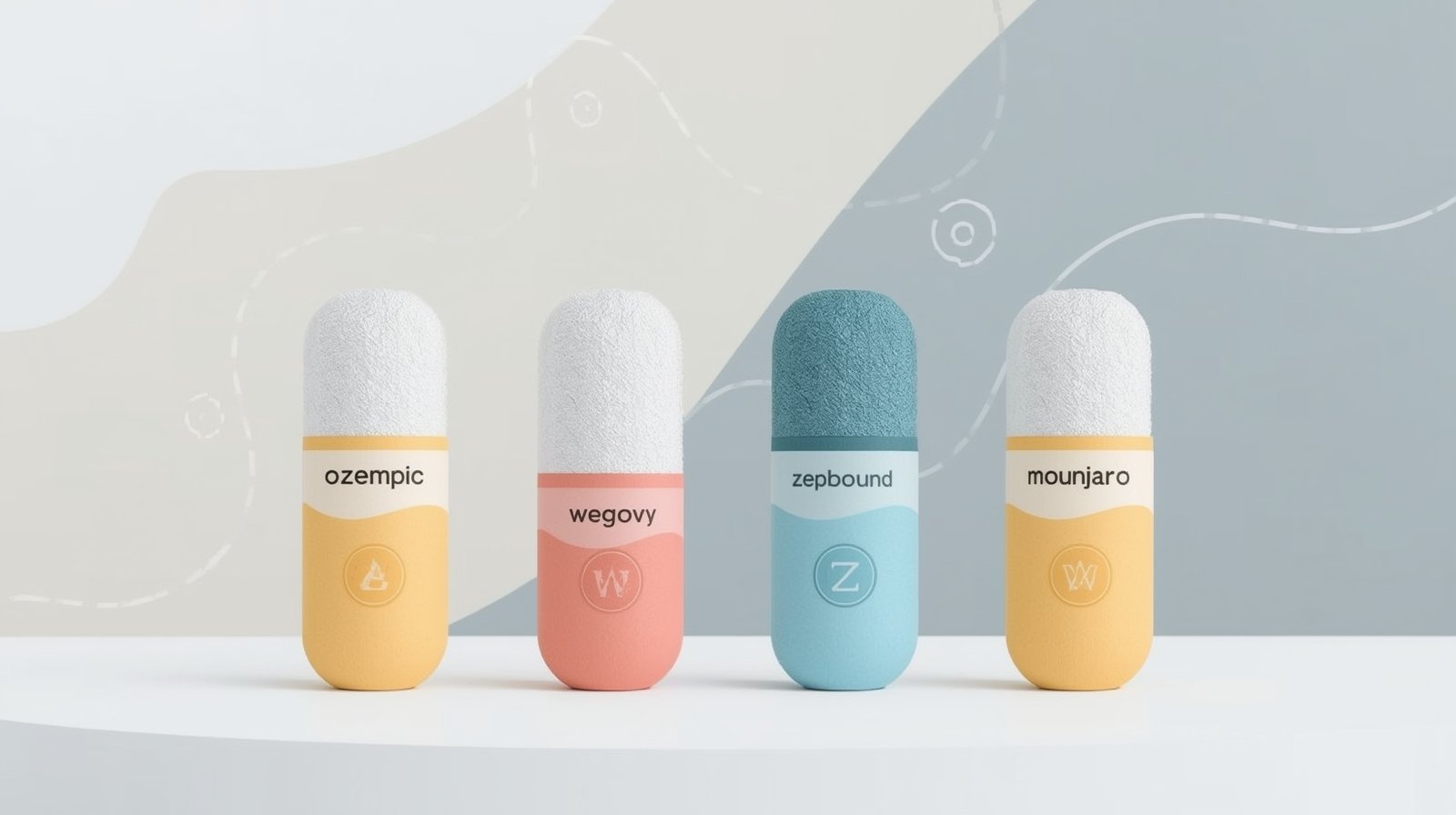
Available GLP-1 Medications in 2025
The landscape of GLP-1 medications has expanded significantly, offering patients multiple options for weight management. Here’s a comprehensive comparison of available options:
Medication Name | Active Ingredient | FDA Approval Date | Dosing Frequency | Average Weight Loss | FDA Approved | Compounded Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Wegovy | Semaglutide | June 2021 | Weekly injection | 15-17% | Yes | Yes |
Ozempic | Semaglutide | December 2017 | Weekly injection | 10-15%* | Yes (diabetes) | Yes |
Zepbound | Tirzepatide | November 2023 | Weekly injection | 20-22.5% | Yes | Limited |
Mounjaro | Tirzepatide | May 2022 | Weekly injection | 15-20%* | Yes (diabetes) | Limited |
Saxenda | Liraglutide | December 2014 | Daily injection | 5-8% | Yes | Yes |
Trulicity | Dulaglutide | September 2014 | Weekly injection | 3-5%* | Yes (diabetes only) | Limited |
*Weight loss percentages for diabetes-indicated medications based on secondary weight loss outcomes in clinical trials.
Important Note: AlynMD provides compounded versions of these medications when brand-name versions are unavailable due to shortages or when medically inappropriate for individual patients. Compounded medications are prepared by licensed compounding pharmacies but are not FDA-approved.
Cost considerations in 2025 show significant variations, with brand-name medications ranging from $900-$1,500 monthly without insurance coverage. Compounded options typically offer more affordable alternatives, though pricing varies by compounding pharmacy and formulation.
Insurance coverage for weight loss indications has expanded in 2025, with many plans now covering FDA-approved obesity medications for patients meeting specific BMI and comorbidity criteria.
Semaglutide Options
Semaglutide represents the most widely prescribed GLP-1 medication, available as Ozempic for diabetes and Wegovy for weight loss. Both contain identical active ingredients but differ in maximum dosing and FDA-approved indications.
The STEP clinical trial program demonstrated remarkable efficacy, with STEP 1 showing an average weight loss of 14.9% compared to placebo over 68 weeks. Participants receiving semaglutide were significantly more likely to achieve 5%, 10%, and 15% weight loss thresholds.
Weekly injection scheduling makes semaglutide convenient for most patients, with dose escalation typically starting at 0.25mg weekly and increasing monthly to minimize side effects. Most patients reach the maintenance dose of 2.4mg weekly (Wegovy) within 16-20 weeks.
Compounded semaglutide through services like AlynMD provides access when brand-name versions face shortages or when patients require customized formulations not available commercially.
Tirzepatide Options
Tirzepatide offers a unique dual mechanism, acting as both a GLP-1 and GIP (glucose dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) receptor agonist. This dual action appears to provide enhanced weight loss compared to single-hormone approaches, making it a compelling option for those seeking personalized health optimization.
The SURMOUNT trial results established tirzepatide as the most effective weight loss medication currently available, with participants achieving average weight losses of 20.9% at the highest dose (15mg weekly) in SURMOUNT-1. These results surpassed all previous weight loss medications.
FDA approval for weight loss came in November 2023 under the brand name Zepbound, following earlier approval as Mounjaro for diabetes treatment. The dual mechanism appears to provide better metabolic benefits and potentially fewer gastrointestinal side effects compared to traditional GLP-1 medications.
Other GLP-1 Medications
Liraglutide (Saxenda) holds the distinction of being the first GLP-1 medication FDA-approved specifically for weight loss in 2014. Despite requiring daily injections, it remains a valuable option for patients who cannot tolerate weekly formulations or prefer more frequent dosing for side effect management.
Dulaglutide (Trulicity) maintains FDA approval only for diabetes treatment, though patients often experience moderate weight loss as a secondary benefit. Its unique delivery device and proven cardiovascular benefits make it popular among healthcare providers for diabetic patients.
Several next-generation medications are advancing through FDA approval processes for 2025-2026, including retatrutide (a triple hormone agonist) and orforglipron (an oral GLP-1 medication), promising even more options for patients.
Side Effects and Safety Profile
Understanding the side effect profile of GLP-1 medications is crucial for setting appropriate expectations and ensuring safe treatment. The most common side effects are gastrointestinal and typically occur during the initial weeks of treatment or dose escalations.
Most Common Side Effects:
- Nausea (reported in 20-44% of patients)
- Vomiting (15-25% of patients)
- Diarrhea (12-20% of patients)
- Constipation (10-15% of patients)
- Upset stomach and stomach pain
- Decreased appetite
These side effects usually peak during the first 4-8 weeks of treatment and often diminish as the body adapts to the medication. Most patients find these symptoms manageable with proper dietary modifications and gradual dose escalation.
Serious but Rare Side Effects:
GLP-1 medications carry FDA warnings for several serious conditions that require immediate medical attention:
- Thyroid tumors: A black box warning exists for potential thyroid cancer risk, based on animal studies.Patients with a personal or family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 or medullary thyroid carcinoma should not use these medications.
- Pancreatitis: Severe stomach pain that may radiate to the back, potentially indicating pancreas inflammation, requires immediate medical attention.
- Gallbladder problems: Rapid weight loss can increase gallstone formation risk, causing severe pain in the upper abdomen.
- Acute kidney injury: Dehydration from vomiting and diarrhea can lead to kidney problems, particularly in patients with existing kidney disease.
- Severe allergic reactions: Though rare, life threatening allergic reactions can occur, requiring emergency medical help.
- Diabetic retinopathy: In diabetic patients, rapid blood sugar improvements may temporarily worsen eye problems.
Managing Common Side Effects:
Successful side effect management significantly improves treatment adherence and outcomes:
- Start with smaller meals and avoid high-fat, greasy foods
- Eat slowly and stop when feeling full
- Stay well-hydrated, especially during episodes of nausea or vomiting
- Consider ginger supplements or anti-nausea medications if recommended by your doctor
- Timing injections in the evening may help reduce daytime nausea
- Gradually increase fiber intake to manage constipation
Some patients experience “Ozempic face,” referring to facial volume loss that may occur with rapid weight loss. This effect is related to fat loss rather than the medication itself and can occur with any significant weight reduction.

Dosing and Administration
Proper dosing and administration techniques are essential for both safety and effectiveness. Most GLP-1 medications follow a gradual dose escalation schedule to minimize side effects while achieving therapeutic levels.
Standard Dose Escalation for Semaglutide (Wegovy):
- Weeks 1-4: 0.25mg weekly
- Weeks 5-8: 0.5mg weekly
- Weeks 9-12: 1.0mg weekly
- Weeks 13-16: 1.7mg weekly
- Week 17+: 2.4mg weekly (maintenance)
Injection Site Management: Rotating injection sites prevents skin irritation and ensures consistent absorption. Approved injection sites include:
- Abdomen (avoid 2-inch area around navel)
- Front of thigh
- Upper arm (if someone else is administering)
Rotate sites weekly and avoid injecting into areas that are tender, bruised, or have scars or stretch marks.
Storage Requirements:
- Refrigerate unopened pens at 36-46°F (2-8°C)
- Do not freeze or shake
- After first use, may be stored at room temperature (59-86°F) for up to 56 days
- Protect from light and heat
- Dispose of pens after 56 days, even if medication remains
Missed Dose Guidelines: If you miss a dose and it’s been less than 4 days, take the injection as soon as you remember. If more than 4 days have passed, skip the missed dose and resume your regular dosing schedule. Never double doses.
Drug Interactions: GLP-1 medications can slow gastric emptying, potentially affecting absorption of other medicines. Key considerations include:
- Birth control pills may have reduced effectiveness if taken close to injection time
- Insulin or other diabetes medications may require dose adjustments to prevent low blood sugar
- Tell your doctor about all other medicines and supplements you take
Clinical Evidence and Research Updates
The evidence supporting GLP-1 medications for weight loss continues to strengthen with ongoing research and real-world data collection. Major clinical trials have consistently demonstrated both efficacy and safety across diverse patient populations.
STEP Trial Program (Semaglutide): The STEP trials represent the largest clinical program for semaglutide in obesity treatment:
- STEP 1: 1,961 participants achieved 14.9% average weight loss over 68 weeks
- STEP 2: Focused on patients with diabetes, showing 9.6% weight loss
- STEP 3: Combined medication with intensive lifestyle intervention
- STEP 4: Demonstrated weight regain after medication discontinuation
SURMOUNT Trials (Tirzepatide): These trials established tirzepatide as the most effective obesity medication:
- SURMOUNT-1: 2,539 participants, average weight loss of 20.9% at highest dose
- SURMOUNT-2: Diabetic participants achieved 13.4% average weight loss
- Results exceeded all previous obesity medications in head-to-head comparisons
American Diabetes Association 2025 Standards of Care (updated January 2025): The latest ADA guidelines provide strong recommendations for GLP-1 receptor agonists:
- First-line therapy for patients with diabetes and obesity
- Preferred agents for patients with established cardiovascular disease
- Recommended for diabetes prevention in high-risk individuals
Cardiovascular Outcome Trials: Recent studies demonstrate significant cardiovascular benefits beyond weight loss:
- SELECT trial (semaglutide): 20% reduction in major cardiovascular events
- STEP-HF trial: Improved heart failure symptoms and exercise capacity
- These findings led to expanded FDA labeling for cardiovascular risk reduction
Long-term Safety Data: Five-year follow-up studies show sustained benefits with continued treatment:
- Weight loss maintenance requires ongoing medication
- No increase in serious adverse events with extended use
- Cardiovascular benefits appear to increase over time
Real-world evidence from electronic health records confirms clinical trial results, with similar weight loss outcomes and side effect profiles in routine clinical practice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are brand name GLP-1 medications available in 2025?
Yes, brand name medications like Wegovy, Ozempic, Zepbound, and Saxenda remain FDA approved and available. However, periodic shortages have affected availability throughout 2023-2025, leading many patients to seek compounded alternatives. Healthcare providers can help determine the best option based on current availability and individual medical needs.
How safe are compounded GLP-1 medications compared to brand versions?
Compounded GLP-1 medications contain the same active ingredients as fda approved brand versions but are prepared by licensed compounding pharmacies rather than pharmaceutical manufacturers. While compounded medications can be safe when prepared by reputable facilities following proper protocols, they may have variability in potency, sterility, and quality compared to FDA-approved versions. The FDA and state pharmacy boards recommend compounded medications only when commercial products are unavailable or medically inappropriate.
What’s the difference between compounded and counterfeit medications?
Compounded medications are legally prepared by licensed pharmacies following state and federal regulations, while counterfeit medications are illegal products that may contain unknown or dangerous ingredients. Compounded GLP-1s are legitimate alternatives when obtained through proper medical channels, whereas counterfeit products often sold online pose serious safety risks.
How long do I need to take GLP-1 medications for weight loss?
Clinical evidence suggests that GLP-1 medications work best as long-term treatments. Most patients need to continue therapy indefinitely to maintain weight loss benefits. Studies show that discontinuing treatment typically leads to weight regain, with 60-80% of lost weight returning within one year. Your healthcare provider can help develop a long-term treatment plan that balances benefits with potential risks.
Can I stop taking GLP-1 medications once I reach my goal weight?
Weight loss maintenance typically requires continued treatment. Clinical trials demonstrate that stopping GLP-1 medications leads to gradual weight regain as appetite and food cravings return to pre-treatment levels. Some patients may be able to reduce dosing frequency or transition to lifestyle-only maintenance, but this should only be attempted under medical supervision.
Are GLP-1 medications safe for long-term use?
Current evidence from clinical trials up to 5 years shows that GLP-1 medications are generally safe for long-term use when properly monitored. The most concerning potential risk is thyroid tumors, though this has only been observed in animal studies. Regular monitoring by healthcare providers helps ensure early detection of any adverse effects.
What happens if I can’t tolerate the side effects?
If you experience severe stomach pain, persistent vomiting, signs of allergic reactions, or other concerning symptoms, contact your doctor immediately. Many side effects improve with slower dose escalation, dietary modifications, or timing adjustments. Your healthcare provider may recommend temporary dose reductions, switching to a different GLP-1 medication, or discontinuing treatment if side effects remain severe.
How do I know if I’m a good candidate for GLP-1 therapy?
FDA-approved criteria for weight loss include having a BMI of 30 or higher, or BMI of 27 or higher with weight related medical problems like high blood pressure, heart disease, or obstructive sleep apnea. Your healthcare provider will evaluate your medical history, current medications, and individual risk factors to determine if GLP-1 therapy is appropriate. Contraindications include personal or family history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome.
Choosing Between Brand and Compounded Options
The decision between brand-name and compounded GLP-1 medications depends on several factors including availability, cost, insurance coverage, and individual medical needs.
When Compounded Medications Are Appropriate: According to FDA guidelines, compounded medications should be considered when:
- FDA-approved commercial products are temporarily unavailable due to shortages
- Patients require dosage strengths not commercially available
- Patients have allergies to inactive ingredients in commercial formulations
- Standard formulations are medically inappropriate for individual patient needs
Quality Standards for Compounding Pharmacies: Compounding pharmacies must operate under strict regulations:
- 503A facilities provide traditional compounding for individual patients
- 503B facilities can produce larger batches under more stringent manufacturing standards
- All facilities must be licensed and regularly inspected by state pharmacy boards
- Reputable compounding pharmacies provide certificates of analysis for their products
Cost Comparison: 2025 pricing typically shows:
- Brand medications: $900-$1,500 monthly without insurance
- Compounded medications: $200-$600 monthly depending on formulation
- Insurance coverage varies significantly, with many plans now covering FDA-approved obesity medications
AlynMD’s Compounded Medication Program: Services like AlynMD work with licensed compounding pharmacies to provide access when commercial products are unavailable. These programs typically include:
- Medical evaluation and prescribing by licensed healthcare providers
- Partnership with accredited compounding pharmacies
- Patient education and support throughout treatment
- Regular monitoring and dose adjustments as needed

When choosing between options, patients should discuss the potential benefits and risks of both FDA-approved and compounded medications with their healthcare providers to make informed decisions.
When to Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Proper medical supervision is essential for safe and effective GLP-1 treatment. Regular communication with healthcare providers ensures optimal outcomes and early detection of potential complications.
Pre-treatment Medical Evaluation Requirements: Before starting any GLP-1 medication, healthcare providers typically assess:
- Complete medical history, including family history of thyroid cancer
- Current medications and potential drug interactions
- Baseline laboratory tests including kidney function and blood sugar levels
- Assessment of weight related medical problems and cardiovascular risk factors
- Discussion of potential benefits versus risks for individual patients
Laboratory Monitoring Schedule: Regular monitoring helps ensure treatment safety and effectiveness:
- Baseline: Complete metabolic panel, HbA1c, lipid profile, kidney function
- 3 months: Follow-up labs to assess metabolic improvements
- 6-12 months: Ongoing monitoring based on individual risk factors
- Annual: Comprehensive evaluation including cardiovascular risk assessment
Emergency Symptoms Requiring Immediate Medical Attention: Contact your doctor immediately if you experience:
- Severe pain in the stomach area that doesn’t go away
- Persistent vomiting preventing fluid intake
- Signs of severe allergic reaction (trouble swallowing, swollen face, fast heartbeat)
- Symptoms of low blood sugar in diabetic patients (pale skin, blurred vision, slurred speech)
- Signs of kidney problems (decreased urination, swelling, fatigue)
- Vision changes or symptoms of diabetic retinopathy
Preparing for Surgery or Other Procedures: GLP-1 medications slow gastric emptying, which can increase risks during procedures requiring anesthesia. Generally:
- Stop medication at least one week before scheduled surgery
- Inform all healthcare providers about GLP-1 use
- Follow specific pre-procedure instructions regarding food intake
- Plan for medication resumption after full recovery
Pregnancy Planning Considerations: Women planning pregnancy should discuss GLP-1 medications with their healthcare provider:
- Stop medication at least 2 months before attempting conception
- Transition to pregnancy-safe weight management strategies
- Consider the impact on birth control pills effectiveness
- Discuss plans for managing weight during and after pregnancy
Regular follow-up appointments allow healthcare providers to monitor progress, adjust dosing, manage side effects, and ensure continued appropriateness of treatment. Open communication about concerns, side effects, and treatment goals helps optimize outcomes while maintaining safety.
The landscape of GLP-1 medications for weight loss continues to evolve rapidly, offering unprecedented opportunities for effective weight management. Whether choosing FDA-approved brand medications or compounded alternatives when appropriate, the key to success lies in proper medical supervision, realistic expectations, and commitment to long-term lifestyle changes. These medications represent powerful tools in the fight against obesity, but they work best as part of a comprehensive approach that includes a reduced calorie diet, regular physical activity, and ongoing medical monitoring.
As we advance through 2025, continued research will further refine our understanding of optimal use, long-term outcomes, and patient selection criteria. For individuals struggling with obesity and weight related medical problems, GLP-1 medications offer hope for achieving and maintaining significant weight loss when used appropriately under medical supervision.