Introduction: Navigating the Evolving GLP-1 Landscape in 2025
The landscape of metabolic health and weight management has been fundamentally reshaped by a class of medications known as GLP-1 receptor agonists. What began as a breakthrough for type 2 diabetes treatment has evolved into a global phenomenon for weight loss, bringing names like Ozempic, Wegovy, Zepbound, and Mounjaro into the mainstream. As we navigate 2025, the options, information, and public discourse surrounding these drugs have reached an all-time high, creating both unprecedented opportunity and significant confusion for those seeking effective treatment.
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing the risk of health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. These medications can play a key role in supporting individuals to reach and sustain a healthy weight, contributing to overall health and well-being.
These medications represent more than just prescriptions; they are powerful tools that interact with the body’s complex hormonal systems to influence appetite, blood sugar, and ultimately, body weight. The choice between them is not as simple as picking a name from a list. It involves understanding different active ingredients, mechanisms of action, FDA-approved indications, and the practical realities of cost and access. This guide is designed to be your authoritative resource, cutting through the noise to provide a clear, comprehensive comparison. If you’re ready to explore treatment options with medical support, you can learn more about GLP-1 agonist medications through AlynMD’s clinically supervised program. We will delve into the science, compare the clinical data, and explore the crucial role of a guided medical journey in achieving sustainable, long-term success.
The Rise of GLP-1 Medications for Weight Management and Diabetes
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are not new; they have been used to treat type 2 diabetes for over a decade. However, their profound effect on weight loss catalyzed a revolution. The market for these drugs is expanding at an astonishing rate, with projections showing it could reach over USD 72,127.79 million by 2034. This explosive growth is fueled by their remarkable efficacy and growing public awareness. As obesity rates continue to be a major public health concern—with an estimated 26.5% of adults in England living with obesity in 2023-2024, for instance—body mass index (BMI) is commonly used to define overweight and obesity, and is a key factor in determining eligibility for new weight loss medications. The result is a rapidly evolving market where new approvals and shifting insurance landscapes make staying informed essential.
Why a 2025 Comparison Guide is Essential for Your Health Journey
In 2025, the choice is no longer just about one or two options. With four major players dominating the conversation—Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound—patients and providers must navigate nuanced differences. Two distinct active ingredients, Semaglutide and Tirzepatide, offer different mechanisms of action and efficacy profiles. Furthermore, these drugs have different FDA-approved uses, creating a critical distinction between treatment for diabetes and treatment for chronic weight management. Understanding these differences is paramount to making an informed decision that aligns with your specific health profile, treatment goals, and the practicalities of insurance coverage and affordability. This guide will help you understand the key differences between these medications, including their approved uses, mechanisms, and insurance coverage, providing the clarity needed to discuss these options confidently with your healthcare provider.
Understanding GLP-1s: The Science Behind the Success
To compare these powerful medications, it is crucial to first understand the underlying science. The success of Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound is rooted in their ability to mimic and amplify the effects of natural hormones in the body that regulate metabolism and appetite. The body makes hormones like GLP-1 and GIP, which play a crucial role in regulating metabolism and appetite.
What are GLP-1 Receptor Agonists? (glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists)
GLP-1 receptor agonists are a class of drugs that mimic the action of glucagon-like peptide-1, an incretin hormone produced in the gut. When you eat, your body naturally releases GLP-1. This hormone signals the pancreas to release insulin (which lowers blood sugar), blocks the release of glucagon (a hormone that raises blood sugar), and slows down gastric emptying, making you feel full for longer.
These medications are “agonists,” meaning they bind to and activate the GLP-1 receptors in various parts of the body, including the pancreas, brain, and digestive tract. By doing so, they replicate and enhance these natural metabolic processes, leading to improved glycemic control and reduced appetite.
How GLP-1 Receptors Impact Your Body: Blood Sugar, Appetite, and Weight Loss
The effects of activating GLP-1 receptors are multifaceted and address several key aspects of metabolic health and weight regulation:
- Blood Sugar Control: By stimulating insulin release only when blood sugar is high and suppressing glucagon, GLP-1s help stabilize glucose levels without the high risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) associated with some other diabetes medications. This is their primary function in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
- Appetite Suppression: GLP-1 receptors are also present in the brain, particularly in areas that control hunger and satiety. By activating these receptors, the medication sends powerful signals of fullness to the brain, reducing food cravings and overall caloric intake. This central nervous system effect is a key driver of weight loss. By reducing appetite and increasing feelings of fullness, these medications help decrease overall food intake, which supports weight loss.
- Delayed Gastric Emptying: The medication slows the rate at which food leaves the stomach. This physical effect contributes to a prolonged feeling of fullness after meals, further reducing the desire to eat.
Together, these three mechanisms create a powerful synergy that promotes significant weight loss and improves metabolic parameters, making these drugs a transformative option for both diabetes and obesity treatment.
Eligibility and Safety: Who Should (and Shouldn’t) Use GLP-1 Medications in 2025
GLP-1 medications like Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound have dramatically changed the landscape of weight management and type 2 diabetes care, offering new hope for people struggling to lose weight and control blood sugar. However, not everyone is a candidate for these powerful weight loss drugs, and understanding eligibility and safety is essential for achieving the best results while minimizing risks.
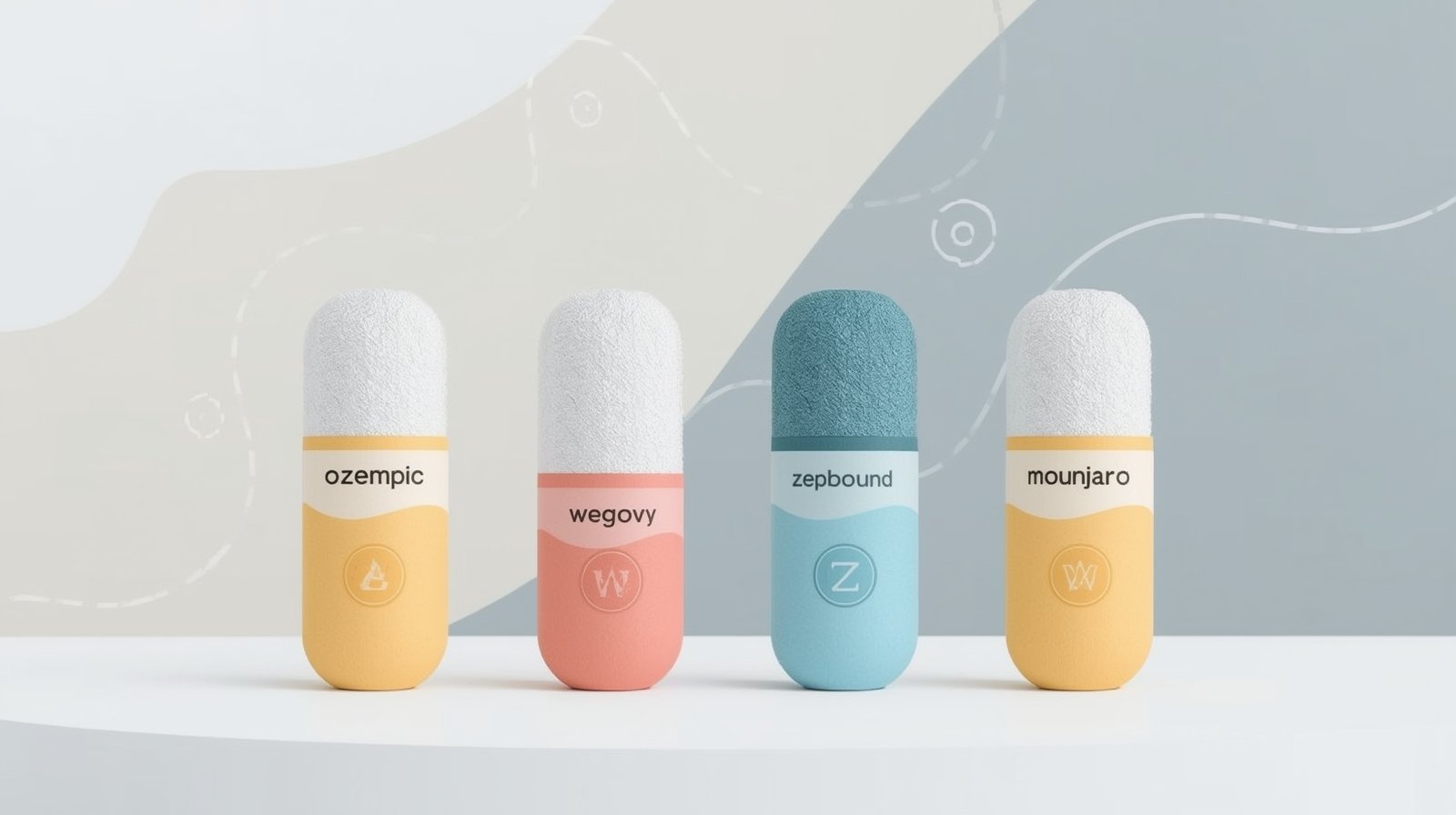
The Main Players: A 2025 Snapshot of Ozempic, Wegovy, Zepbound, and Mounjaro
While all four medications fall under the umbrella of incretin mimetics, they are not interchangeable. They are divided into two pairs, each based on a unique active ingredient: Semaglutide and Tirzepatide.
Some of these medications, such as Wegovy and Ozempic or Zepbound and Mounjaro, are essentially the same drug but are marketed under different brand names for specific indications.
Ozempic (Semaglutide): Primarily for Type 2 Diabetes Management
- Active Ingredient: Semaglutide
- Mechanism: GLP-1 Receptor Agonist
- FDA Approval: Approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes to improve glycemic control in adults. It is also approved to reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (like heart attack or stroke) in adults with type 2 diabetes and known heart disease. Ozempic is typically prescribed at a lower dose for blood sugar control, while higher doses of semaglutide are used in other medications for weight management.
- Use for Weight Loss: While not officially approved for weight loss, its significant weight loss effects have led to widespread “off-label” prescribing for this purpose. Ozempic remains a dominant force in the market, capturing close to 60% of the GLP-1 receptor agonist category.
Wegovy (Semaglutide): The Established Weight Loss Medication
- Active Ingredient: Semaglutide
- Mechanism: GLP-1 Receptor Agonist
- FDA Approval: Specifically approved for chronic weight management in adults with obesity (BMI ≥30) or who are overweight (BMI ≥27) with at least one weight related condition, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or type 2 diabetes. These weight-related conditions are common comorbidities that qualify patients for Wegovy. It is also approved for use in adolescents aged 12 and older with obesity.
- Key Distinction: Wegovy is essentially a higher-dose version of Ozempic, formulated and studied specifically for weight loss. Its maximum dose (2.4 mg) is higher than the standard maximum diabetes dose of Ozempic (2.0 mg).
Mounjaro (Tirzepatide): Dual-Action for Type 2 Diabetes
- Active Ingredient: Tirzepatide
- Mechanism: Dual GLP-1 and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) Receptor Agonist
- FDA Approval: Approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes to improve glycemic control in adults.
- Use for Weight Loss: Like Ozempic, Mounjaro demonstrated exceptional weight loss in clinical trials, leading to its frequent off-label use for weight management before its counterpart, Zepbound, was approved. Its dual-action mechanism is a key differentiator.
Mounjaro vs other medications is a frequent topic of discussion, as patients and providers compare its dual-action mechanism and efficacy to other available options.
Zepbound (Tirzepatide): The Latest Frontier in Obesity Treatment
- Active Ingredient: Tirzepatide
- Mechanism: Dual GLP-1 and GIP Receptor Agonist
- FDA Approval: Approved in late 2023 for chronic weight management in adults with obesity (BMI ≥30) or who are overweight (BMI ≥27) with a weight-related comorbidity. Zepbound is a new weight loss drug recently approved by the FDA, providing a novel option for obesity treatment.
- Key Distinction: Zepbound is the exact same medication as Mounjaro, just marketed under a different brand name and packaged for its specific indication of weight management. It offers the same range of doses and dual-action benefits.
Head-to-Head Comparison: Key Differentiators for 2025 Decision-Making
Choosing the right medication requires a deeper dive into the factors that set these drugs apart. From their core biological function to clinical efficacy and side effect profiles, these differences can significantly impact a patient’s experience and outcomes. It is also important to note that the side effect profiles and risks of these medications may differ from those of other weight loss drugs, which patients should carefully consider.
Mechanism of Action: Semaglutide (GLP-1) vs. Tirzepatide (GLP-1/GIP)
The most fundamental difference lies in their active ingredients and the receptors they target.
Semaglutide (Ozempic and Wegovy) is a pure GLP-1 receptor agonist. It focuses solely on activating the GLP-1 pathway to control blood sugar, suppress appetite, and slow digestion. This single-receptor approach has proven highly effective for both diabetes management and weight loss. Some medications, such as Ozempic and Wegovy or Mounjaro and Zepbound, contain the same active ingredient but are approved for different medical conditions.
Tirzepatide (Mounjaro and Zepbound) is a first-in-class dual-agonist. It activates both the GLP-1 receptor and the GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) receptor. GIP is another incretin hormone that plays a role in insulin secretion and may have complementary effects on energy balance and fat metabolism. By targeting two distinct hormonal pathways, Tirzepatide creates a synergistic effect that clinical trials suggest can lead to superior glycemic control and greater overall weight loss compared to GLP-1 agonists alone.
Approved Indications and Evolving Off-Label Use in 2025
The distinction between FDA-approved (“on-label”) use and “off-label” use is critical for understanding insurance coverage and treatment rationale.
- For Type 2 Diabetes: Ozempic and Mounjaro are the on-label options.
- For Chronic Weight Management/Obesity: Wegovy and Zepbound are the on-label options.
In 2025, the practice of prescribing diabetes-indicated drugs like Ozempic and Mounjaro for weight loss remains common, especially when patients face insurance hurdles or supply shortages for Wegovy and Zepbound. However, insurers are increasingly cracking down on this practice, often requiring a formal type 2 diabetes diagnosis for coverage. This regulatory landscape makes the distinction between the brands more important than ever. The rise in prescriptions for these drugs is significant; one analysis showed that from 2018 to 2023, semaglutide prescriptions rose to 63% of GLP-1 RA prescriptions in non-diabetic individuals who are obese or overweight.
Efficacy for Weight Loss and Blood Sugar Control (Clinical Trials and Real-World Implications for 2025)
Clinical trials provide the best head-to-head evidence of these drugs’ effectiveness.
- Weight Loss: In pivotal trials, semaglutide (Wegovy) led to an average body weight loss of around 15%. Tirzepatide (Zepbound) has shown even greater efficacy, with participants achieving an average weight loss of over 20% at the highest dose. To put it in perspective, when considering how much weight participants lost, those on tirzepatide lost up to 52 pounds on average, depending on the starting weight and dose. While individual results will always vary, this data suggests tirzepatide may offer a more potent option for individuals with higher weight loss goals.
- Blood Sugar Control: Both semaglutide and tirzepatide are highly effective at lowering HbA1c (a measure of long-term blood sugar control). Head-to-head studies in patients with type 2 diabetes have generally shown that tirzepatide leads to slightly greater reductions in HbA1c compared to semaglutide.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: Beyond weight and glucose, these medications offer significant heart health benefits. The landmark SELECT trial demonstrated that semaglutide reduced the risk of heart attack, stroke, or cardiovascular death by 20% in patients with overweight or obesity and pre-existing cardiovascular disease, even if they did not have diabetes. This positions semaglutide as a proven option for cardiovascular risk reduction. Similar outcome trials for tirzepatide are ongoing and highly anticipated. These proven results highlight why GLP-1 agonist medications have become a cornerstone of modern weight management and metabolic health treatment when combined with comprehensive medical supervision.
Dosing Schedules and Administration: Convenience and Consistency
All four medications are administered as a once-weekly subcutaneous (under the skin) injection using a user-friendly pen device. These are injectable medications, not pills. Injections can be given in the upper arm, belly, or thigh, depending on patient preference. The key aspect of administration is the titration schedule.
Treatment for all four drugs begins at a low starting dose to allow the body to acclimate and minimize side effects. The dose is then gradually increased, typically every four weeks, until a target maintenance dose is reached. These medications are available in different doses to accommodate individual needs.
- Semaglutide (Ozempic/Wegovy): Starts at 0.25 mg weekly and titrates up to a maximum maintenance dose of 2.0 mg (Ozempic for diabetes) or 2.4 mg (Wegovy for weight loss).
- Tirzepatide (Mounjaro/Zepbound): Starts at 2.5 mg weekly and titrates up in 2.5 mg increments to a maximum maintenance dose of 15 mg. Zepbound is available as an injectable medication in three doses, administered once weekly.
A slow and steady titration managed by a healthcare provider is crucial for tolerability and long-term adherence.
Side Effects, Tolerability, and Risks: What to Expect in 2025
The side effect profiles for both semaglutide and tirzepatide are very similar, primarily affecting the gastrointestinal system.
- Common Side Effects: The most frequent side effects are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, and decreased appetite. These are typically most pronounced when starting the medication or increasing the dose and tend to lessen over time for most people.
- Serious Risks: While less common, there are serious risks to be aware of. These include a risk of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), gallbladder problems (gallstones), and kidney injury. There is also a boxed warning for a risk of thyroid C-cell tumors, based on studies in rodents. Due to this risk, these drugs are contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2).
Managing these effects is a key part of the treatment journey. A healthcare provider can offer strategies like dietary modifications and adjusting the titration schedule to improve tolerability.
It is important to note that stopping these medications often leads to weight regain, with many patients regaining a significant portion of lost weight within a year or two if treatment is discontinued.
The Practical Realities: Cost, Coverage, and Access in 2025
Beyond the clinical differences, the practical aspects of obtaining these medications are often the biggest challenge for patients. The landscape of cost, insurance, and availability is complex and constantly in flux. Many insurance plans have different policies regarding coverage for weight loss medications, so it is important for patients to check their specific plan.
Understanding GLP-1 Medication Costs and Pricing
Without insurance, the list price for a one-month supply of any of these four medications can be over $1,000. This high cost makes insurance coverage a necessity for most patients. Eli Lilly is the manufacturer of Mounjaro and Zepbound, and plays a significant role in the pricing and availability of these medications. The debate around their value is ongoing. While these drugs can lead to significant health improvements, potentially reducing medical costs by an estimated $560 per user per year, they also dramatically increase prescription spending. Some analyses have argued that prices would need to be significantly reduced to be considered cost-effective by traditional standards, with one study suggesting tirzepatide would need a 30% price reduction to meet certain thresholds.
Navigating Insurance Coverage in 2025 (Commercial, Medicare, and Employer Plans)
Insurance coverage is the single biggest barrier to access. In 2025, insurers have established strict criteria for approval:
- Prior Authorization (PA): Virtually all plans require a prior authorization. This process involves your doctor submitting documentation to the insurance company to justify the medical necessity of the prescription.
- Indication-Specific Coverage: Insurers are increasingly enforcing on-label use. They will often cover Ozempic/Mounjaro only with a type 2 diabetes diagnosis and Wegovy/Zepbound only for patients meeting the specific BMI and comorbidity criteria for chronic weight management.
- Step Therapy: Some plans may require you to try and fail other, less expensive weight loss medications or other medications before they will approve a GLP-1. This means you may need to demonstrate that other medications were not effective or suitable prior to getting coverage for a GLP-1 receptor agonist.
- Employer Opt-Outs: Many employer-sponsored health plans have chosen to exclude anti-obesity medications from their formularies altogether due to the high cost. Medicare Part D plans generally do not cover medications for weight loss, though this is a subject of ongoing legislative debate.
Availability and Supply Chain Considerations for 2025
The unprecedented demand for these drugs has led to persistent, widespread shortages. Manufacturers have struggled to scale up production to meet the demand, resulting in backorders for many dose strengths. These shortages can disrupt treatment, forcing patients and providers to switch medications or pause therapy. While manufacturers are investing billions in new production facilities, it is anticipated that intermittent supply issues will continue throughout 2025, requiring flexibility and proactive communication with your pharmacy and healthcare provider.
The Role of Compounded GLP-1s: A Deep Dive for 2025
In response to high costs and shortages, some patients have turned to compounded versions of semaglutide and tirzepatide. Compounding pharmacies create custom medications by mixing active pharmaceutical ingredients. While legal in specific circumstances, such as during a formal drug shortage, the FDA has issued warnings about the safety and efficacy of these products. Compounded versions are not FDA-approved and may use different salt forms of the active ingredient (e.g., semaglutide sodium) that have not been studied for safety or effectiveness. There is no guarantee of purity, potency, or sterility, posing potential risks to patients.
Your GLP-1 Journey: Beyond the Prescription in 2025
Successfully using a GLP-1 medication involves more than just a weekly injection. These drugs are a tool, not a cure-all. Achieving sustainable results requires a comprehensive approach that integrates medication with lifestyle changes and ongoing medical support. Combining GLP-1 medications with a healthy diet is crucial for achieving and maintaining weight loss, as nutritional improvements and eating fewer calories can enhance the effectiveness of treatment. Recent data shows that patient persistence is improving, with approximately 63% of patients initiating Wegovy or Zepbound in early 2024 remaining on therapy at one year, but this highlights that a significant portion still discontinues treatment.
The Crucial Role of Lifestyle Changes for Sustainable Progress
To maximize the benefits of any GLP-1 medication and maintain results long-term, lifestyle modifications are non-negotiable.
- Nutrition: The medication helps control appetite, creating an opportunity to build healthier eating habits. Focusing on a balanced diet rich in protein, fiber, and healthy fats can enhance satiety, preserve muscle mass during weight loss, and provide essential nutrients. Losing excess weight can also help lower the risk of conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise is vital for improving metabolic health, building muscle, and boosting mood. A combination of cardiovascular exercise and strength training is ideal.
- Behavioral Strategies: Understanding the psychological aspects of eating is key. A comprehensive program should address habits, emotional eating triggers, and stress management techniques to build a new, healthier relationship with food.
Finding the Right Healthcare Provider and Support Team
Navigating a GLP-1 journey alone can be challenging. The ideal healthcare partner is not just a prescriber but a comprehensive support system. Look for a provider or program that offers:
- Expert Medical Management: A clinician who can help you choose the right medication, manage the titration schedule to optimize for efficacy and tolerability, and monitor for side effects.
- Personalized Coaching: Access to nutritionists or health coaches who can provide tailored guidance on diet and exercise.
- Ongoing Support: Regular check-ins to track progress, make adjustments, and provide accountability and encouragement.
Setting Realistic Goals and Tracking Progress
Success is about more than the number on the scale. While weight loss is a primary goal, it is important to set realistic expectations and celebrate other victories. Track progress in multiple ways:
- Body Measurements: Changes in waist circumference can be a great indicator of fat loss.
- Health Markers: Monitor improvements in blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
- Non-Scale Victories: Pay attention to increased energy levels, improved mobility, better sleep, and clothes fitting more comfortably.
Making an Informed Decision: Which GLP-1 is Right for You in 2025?
With a thorough understanding of the science, clinical data, and practical realities, you can work with your healthcare provider to make a truly informed choice. Eligibility for these medications often depends on your specific health condition, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or Type 2 diabetes, so it’s important to discuss your health condition with your healthcare provider. The “best” medication is the one that aligns with your individual health profile, goals, and access.
A Decision Framework: Considering Your Goals, Health Profile, and Preferences
Ask yourself and discuss these questions with your doctor:
- What is my primary diagnosis? Do I have type 2 diabetes, or is my primary goal chronic weight management? This will heavily influence which medication is most appropriate and likely to be covered by insurance.
- What are my weight loss goals? If you have a significant amount of weight to lose, the potentially higher efficacy of a dual-agonist like tirzepatide might be a deciding factor.
- What does my insurance cover? This is often the most practical and limiting factor. Your provider’s office can help you investigate your formulary and prior authorization requirements.
- Do I have other health conditions? If you have a history of cardiovascular disease, the strong evidence from the SELECT trial might make semaglutide a compelling choice.
When to Consider Semaglutide (Ozempic/Wegovy)
- You have a confirmed type 2 diabetes diagnosis (Ozempic).
- Your primary goal is weight loss, and your insurance specifically covers Wegovy.
- You have a history of cardiovascular disease, and the proven cardiovascular risk reduction is a priority.
- You prefer a medication with a longer track record and more extensive real-world data.
When to Consider Tirzepatide (Mounjaro/Zepbound)
- You have both type 2 diabetes and significant weight loss goals, making Mounjaro’s dual benefits highly attractive.
- Tirzepatide has demonstrated substantial weight loss in clinical trials, showing superiority over other medications like Wegovy and Ozempic.
- Tirzepatide is effective at helping patients lower blood sugar and improve blood glucose control, making it a strong option for those managing type 2 diabetes.
- Zepbound is approved for use in adults with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea and obesity, offering dual treatment benefits.
- Your primary goal is weight management, you meet the BMI criteria, and your insurance covers Zepbound.
- You have previously tried a GLP-1 medication like semaglutide and did not achieve your desired results.
- You are seeking the highest potential efficacy for weight loss based on current clinical trial data.
Final Thoughts
The emergence of Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound has marked a paradigm shift in the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes. As we look ahead in 2025, these medications offer powerful hope and proven results. However, their effectiveness is maximized when they are part of a comprehensive, medically supervised plan. The choice between semaglutide and tirzepatide is a nuanced one, hinging on a careful consideration of your unique medical needs, insurance landscape, and personal health goals.
The journey is not just about the prescription; it is about building sustainable habits, managing side effects proactively, and having a dedicated support system to guide you. The data shows that adherence is key, and adherence is best supported by a holistic approach that combines powerful medication with personalized coaching and expert medical oversight.
Ultimately, the most important step is to have an open, informed conversation with a qualified healthcare provider. AlynMD offers personalized GLP-1 treatment programs that combine expert medical oversight with comprehensive support to help you achieve lasting results. By arming yourself with the knowledge in this guide, you can confidently partner with them to select the right path forward, leveraging these incredible tools to achieve lasting improvements in your health and well-being.