



Here are some common reasons why testosterone might be low on a blood test:
Here are some symptoms that may be linked to low testosterone levels:
Here are a few general strategies that may help support healthy testosterone levels:
Here are some common reasons why testosterone might be high on a blood test:
Here are some symptoms that might be linked to high testosterone levels:
Here are a few strategies that might help support healthy testosterone levels:

Here are a few signs or situations when it’s a good idea to speak with a healthcare provider about your testosterone levels:
Here are a few related blood markers or areas to ask your doctor about if testosterone levels are abnormal:
Here are a few important reminders to keep in mind when interpreting lab results:
Answer 1
Answer 2

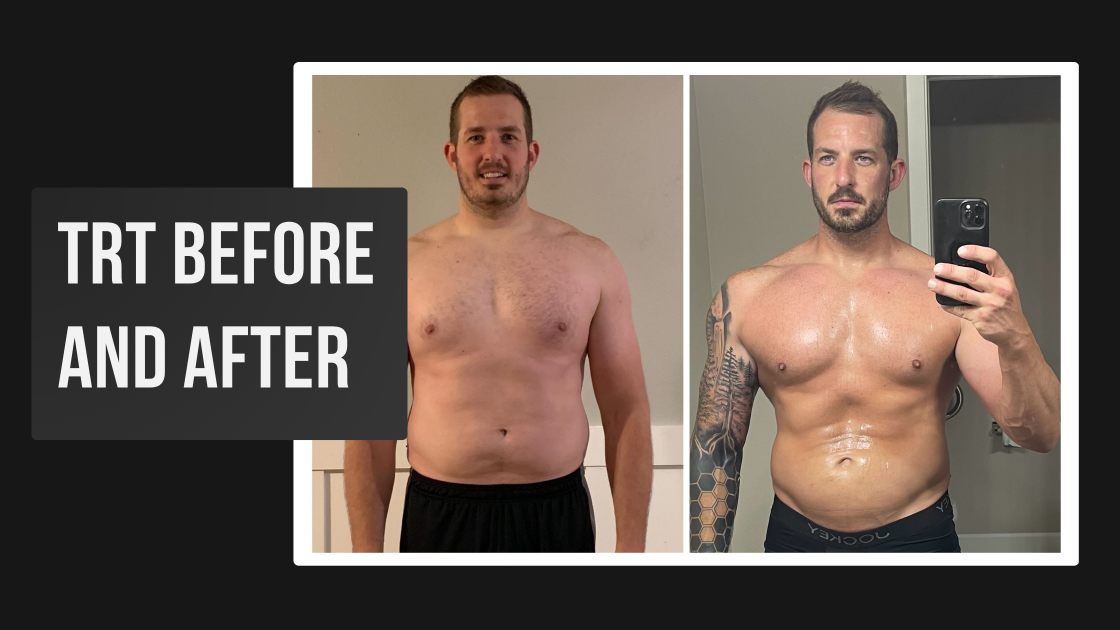
























Copyright © 2026. Alyn MD. All rights reserved.